Research Reports
Early Detection of Lung Cancer in India and Other Underserved Populations
qure.ai Impact White Paper
April 26, 2022
Executive Summary of Report
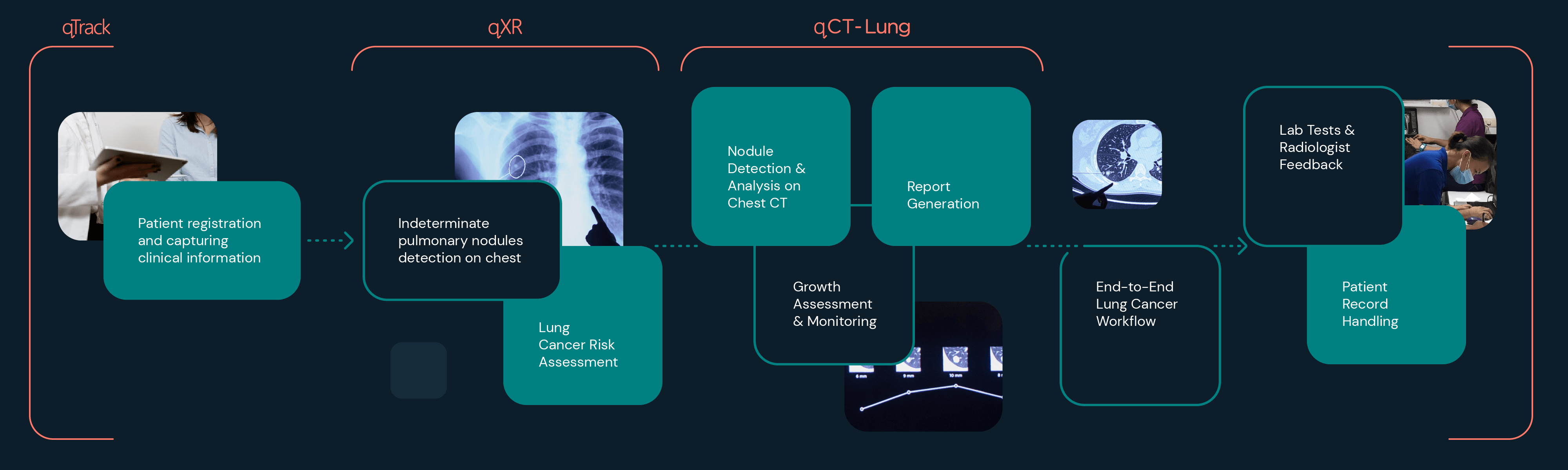
Qure.ai is a Mumbai-based company engaged in developing artificial intelligence (“AI”) for X-ray (“XR”), computed tomography (“CT”), and other imaging modalities for use in Low-, Middle-, and High-income countries. To date, it has scaled to 50 countries/5 continents; has an AI repository of ~1B images; scans
~4M patients annually (and growing); and has a mission (among others) to help mitigate the alarming global problem of late lung cancer diagnosis and related premature mortality.FN1 Its primary revenue to date derives from its XR imaging AI, which assists in detecting and localizing almost 30 lung disease abnormalities, including suspicious nodules for triage to lung cancer detection via CT, biopsy, and other standards of care.
The Objectives of this White Paper are two-fold:
- to provide an overview of lung cancer burdens; risk factors associated with that disease; and principal barriers to lung cancer detection in India; and
- to describe the potential impact of Qure’s XR AI, intended to help earlier identification of suspicious nodules for lung cancer detection follow-up – a key offering provided by Qure.ai.FN2
Throughout this report, there are several overarching themes, foremost among them the urgent need in India to create more and better avenues, however indirect, for earlier identification of suspicious lung nodules requiring follow-up.
Equally vital is the need to retool existing resources, including portable and other forms of XR prevalent in India, so that they can provide more meaningful assistance with earlier identification of suspicious lung nodules. It is our view that India will not have the capacity to overhaul its existing cancer care infrastructure with significant expenditures on detection equipment, comprehensive screening programs, and additional trained specialists – particularly post-COVID, but perhaps ever. For this reason, we also believe AI of the type developed by Qure.ai will be an important, pragmatic solution that could help reduce the alarming late presentation and premature mortality that all too often attend this disease in India.
Several introductory points regarding Qure’s potential impact are warranted:
- Although we focus on XR, Qure also has AI to facilitate second-step CT lung cancer screening as well. As noted, this AI is currently registered in
~50+ countries, including numerous Low- and Middle-Income Countries (“LMICs”). However, our report’s discussion is confined primarily to XR, because we believe XR is the critical step needed to affect significant improvement in earlier cancer detection for India and other LMICs. XR- agnostic AI, in our view, will offer the greatest impact because, among other reasons:
(a) there is considerably greater availability of XR imaging systems in LMICs than more costly CT imaging, and there are now portable XR systems as well that allow more expanded point-of-care reach;
(b) XR imaging in India is typically a patient’s first point of contact in the cancer journey – often incidentally for unknown chest/lung concerns;
(c) more healthcare personnel are trained to operate the basics of this imaging system, than are trained on other modalities, including CT;
(d) XR imaging is inherently less accurate than CT in finding suspicious nodules, and thus will benefit most from AI interpretation assistance; and
(e) there are significant global health programs underway that support improved identification of tuberculosis and other diseases of the lung in LMICs. Under these programs (e.g., a multi-continent, 5-year initiative funded by The Global Fund), Qure’s AI is deployed on the same equipment and at the same time, to leverage greater identification and localization of lung cancer, TB, and other lung diseases/abnormalities. Results have been sufficiently impressive that the WHO has endorsed the AI as an alternate to human readers for TB. To our awareness, this is the first time a regulatory body has endorsed an AI imaging scan as an alternative (versus a complement) to specialist interpretation.
- Although the burden of lung cancer is significant, not least because of unacceptably high premature mortality rates in LMICs, the company’s impact does not rest on this cancer alone. There has been, or will be, multiple diseases addressed by Qure.ai’s ambitious XR and CT AI development efforts, including SARS-CoV-2, tuberculosis (which has symptomology often confused with lung cancer), COPD, heart failure, stroke, and trauma, among other diseases. There are also expected to be AI enhancements for other diagnostic modalities, including mammography and point-of-care ultrasound systems (“POCUS”).
- We are highlighting lung cancer principally because, as noted, this cancer does not have adequate screening tools for early identification in LMICs and other Underserved Populations; it is diagnosed too late too often; and the global community has come to see lung cancer as an early case study for the transformative potential of AI-assisted cancer imaging in Low-Resource, Underserved Settings.
- Although, for the sake of brevity, we focus on one of TEAMFund’s principal target countries, India, to expand our impact thesis, there are now a total of 50+ countries that have benefitted from Qure’s AI. A number of these are LMICs – for example, the Philippines, Cambodia, Malawi, Pakistan, Myanmar, Nigeria, and Kenya, to name but several. Should we decide to invest, this would also be the first portfolio company to have demonstrated significant scaling to Latin America, a continent of potential interest for Fund II.
-
Notable as well, the company has made significant leapfrog penetration in High-Income Countries (“HICs”) with a focus on Underserved Populations. Indeed, if we were to invest, this company would represent the most advanced case of leapfrog commercialization in our portfolio. The lead example is the UK, where radiologists are in short supply, and production of definitive radiological reports can be delayed by up to a couple months.
The Qure.ai system could potentially reduce the amount of time from first chest X-ray to cancer diagnosis from 60 to 30 days, preliminary UK studies suggest.FN3 At the moment, the UK population typically waits two or more days for their X-ray result, and then needs to make a separate CT appointment if there is a risk they may have cancer. As a consequence, many cases of lung cancer are only spotted at a late stage, and a third of those diagnosed with the disease in the UK, die within 90 days. Even the smallest delay, thus, can move patients from early stage disease, when curative treatment is possible, to later stage lung cancer, when the prospects for life-saving treatments grow increasingly dim.
Qure’s XR AI may also identify more suspicious nodules than the human eye.FN4 In the UK, around 9,300 lung cancer cases a year are missed in chest X-rays, because certain lung nodules can be extremely difficult to spot, particularly in overburdened radiology settings. The hope, thus, is that AI, when used to complement radiology and teleradiology, could also pick up some of those cases earlier as well.FN5
-
To tell the story of Qure.ai and its potential impact:
- In Section II, we review the burdens of lung cancer, both globally and in India, and briefly summarize key risk factors for the disease; and
- In Section III, we discuss principal challenges to accessing early lung cancer detection in India, including:
- awareness, cultural, and social disparity impediments;
- suboptimal prevention activities to address tobacco consumption, the major modifiable risk factor for lung cancer;
- time, distance, and affordability barriers to access early testing;
- quality concerns with respect to XR imaging; and
- scarcity of radiologists.
It is recognized that challenges with respect to cancer treatment also exist in India – substantially so for the poor and the more vulnerable. Although for many Indians, there is access to acceptable cancer care in urban settings, referral tertiary care hospitals, and select public hospitals,FN6 for all too many of the population, the affordability concerns, specialist shortages, and other cancer detection challenges discussed in this report, also harm access to cancer treatment. We leave that discussion for another White Paper, as it is beyond the scope and purpose of this report. It is our hope, however, that increased attention to cancer diagnosis led by companies like Qure.ai, will shine a light on the need for improved access to the entire continuum of cancer care. As one example of this increased spotlight, a significant collaboration between Qure and AstraZeneca is now underway, to help promote better coordination of both diagnosis and treatment options in Underserved Populations.FN7
- Finally, in Section IV and V, we summarize very briefly key aspects of Qure.ai’s technology that contribute to this impact thesis.FN8 We also offer several forward-looking thoughts on expected future advances in lung cancer diagnosis and their relationship to radiological devices, and then conclude with proposed metrics for impact monitoring.
Please contact c.haynes@teamfundhealth.org to request access to the full report.
Footnotes
FN1 TB and COVID are also significant global health uses of Qure’s XR imaging AI.
FN2 Qure.ai is a Mumbai-based company with proprietary AI systems that assist in interpreting, triaging, and/or screening X-ray (“XR”) and computed tomography (“CT”) scans, and in due course other modalities (e.g., ultrasound) as well. Indications for use depend on AI-specific regulatory clearances and thus will vary by geography and be iteratively expanded/refined over time. Please refer to Section IV and Investment Documentation for a further discussion of Qure.ai’s commercial and R&D offerings.
FN3 Bawden, Tom. NHS to trial AI system that could cut lung cancer diagnosis time by half. inews. February 28, 2022. https://inews.co.uk/news/science/nhs-trial-ai-system-cut-lung-cancer- diagnosis-time-half-1465149.
FN4 See, e.g., Prayer, F., et al. Artificial intelligence in lung imaging. Radiologe. 2020 Jan;60(1):42-47. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31754738/
FN5 Id.
FN6 As one example of progress in treating lung cancer, there is a relatively high prevalence of EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements in India, and generic versions of some of the EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors are available at considerably lower cost, including at some government-run hospitals. Also, where patient costs are prohibitive, there are a number of payment assistance programs available, including universal care coverage; the Ayushmann Bharat initiative; and State-run programs for the most vulnerable. See, e.g., Singh, Navneet, MD, DM, et al. Lung Cancer in India. Journal of Thoracic Oncology. August 1, 2021. https://www.jto.org/article/S1556-0864(21)01704-4/fulltext. Devi, Ratna. Renewed challenges in cancer care: Learnings from the COVID pandemic. Financial Express. January 12, 2022. https://www.financialexpress.com/healthcare/covid-19/renewed-challenges-in-cancer-care- learnings-from-the-covid-pandemic/2404454/. Kalpathi, Krishnamani, MD. Lung cancer in India. ecancer. February 22-27, 2022. https://ecancer.org/en/video/10192-lung-cancer-in-india. Agrawal, Shreya. World Cancer Day 2022: Recognising and understanding the inequities in cancer care in the country. Indian Express. February 4, 2022. https://indianexpress.com/article/lifestyle/health/world-cancer-day-2022-theme-close-the-care- gap-inequities-cancer-care-india-7754787/. Singh, Navneet, MD, DM. Cancer in my community: India’s unique cancer care challenges. Cancer.net. November 21, 2019. https://www.cancer.net/blog/2019-11/cancer-my-community-indias-unique-cancer-care- challenges.
FN7 Although currently in Latin America, Turkey, Malaysia, Philippines, and the Middle East, it is hoped that this type of Pharma collaboration will be expanded into India and other LMICs as well.
FN8 For greater details about the company, please refer to investment documentation.